2023.04.03
Force production mechanism for dendritic cell migration
System Neurobiology and Medicine・ Assistant Professor ・ Kentarou Baba
Dendritic cell (DC) is one of immune cells. DCs take antigens and then move to dermis tissue from epidermis tissue. And then, DCs migrate throw lymph duct to reach lymph node. Finally, DCs migrate to chemokine source side to present the antigen information to T-cells (Figure 1) 1). Dendritic cell migration is important for the immune system. Disturbing of dendritic cell chemotaxis cause immunological deficiency syndrome 2, 3). This patient has reduction of the resistance for bacteria 2, 3). However. it is unclear how dendritic cell produces the force (traction force) for cell migration. Our laboratory found that shootin1 molecule is involved in the mechanism of force production for cell migration. I introduce the shootin1-mediated molecular mechanism of dendritic cell migration.
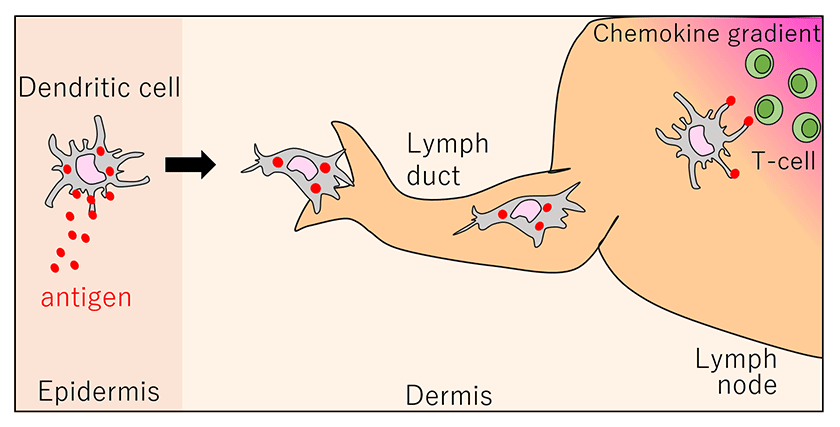
Figure 1. Dendritic cell migration in vivo:
Dendritic cell (DC) is one of immune cells. DCs take antigens and then move to dermis tissue from epidermis tissue. And then, DCs migrate throw lymph duct to reach lymph node. Finally, DCs migrate to chemokine (CCL19) source side to present the antigen information to T-cells.
References
- Worbs T, Hammerschmidt S, Forster R. Dendritic cell migration in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017; 17(1); 30-48
- Ato M, Maroof A, Zubairi S, Nakano H, Kakiuchi T, Kaye P. Loss of Dendritic Cell Migration and Impaired Resistance to Leishmania donovani Infection in Mice Deficient in CCL19 and CCL21. J. Immunol. 2006; 176(9): 5486-5493
- Gutierrez-Kobeh L, Rodriguez-Gonzalez J, Argueta-Donohue J, Vazquez-Lopez R, Wilkins-Rodriguez A. Role of Dendritic Cells in Parasitic Infections. IntechOpen. 2018; 79491: 47-78
Kentarou Baba NAIST Edge BIO, e0011. (2023).
