2022.08.01
Role of methylated DNA-binding proteins in embryonic development and cellular differentiation
Functional Genomics and Medicine ・ Assistant Professor ・ Eishou Matsuda
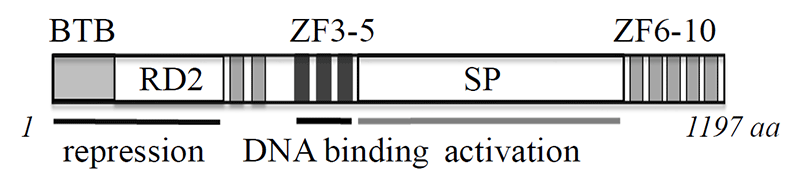
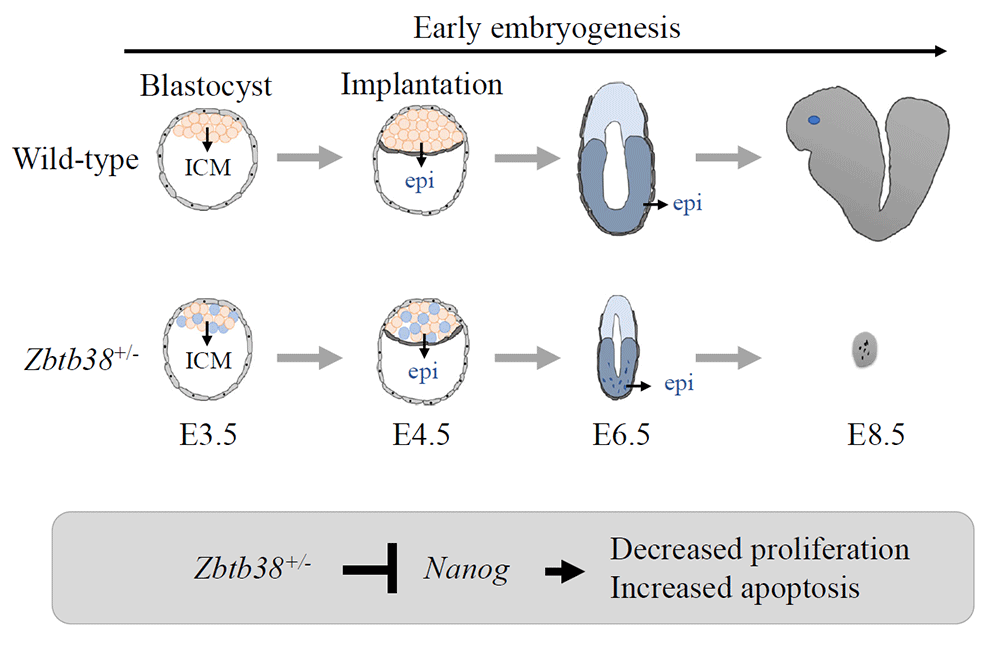
Genetic information comprises genomic DNA sequence information and genetic information called epigenetics, which is becoming increasingly important in mammals. Epigenetics are mechanisms that control gene expression and cellular phenotypes with no changes in the DNA sequence. One of the leading players in epigenetics is DNA methylation, which is essential for various life phenomena such as cell-specific and time-specific regulation of gene expression, embryonic development and cellular differentiation, etc. Aberrations in DNA methylation cause abnormalities in normal embryonic development and cell differentiation, leading to various diseases such as cancer and neurological abnormalities.Here, we introduce the novel methylated DNA-binding protein Zbtb38 that we have identified.
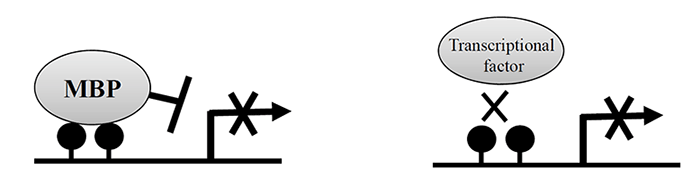
Figure1. Mechanisms by methylated CpGs of gene promoters
Left: MBP binds to methylated CpGs and represses transcription
Right: Methylated CpGs inhibit transcription factor binding
●| : methylated CpG
Eishou Matsuda NAIST Edge BIO, e0003. (2022).