2024.03.01
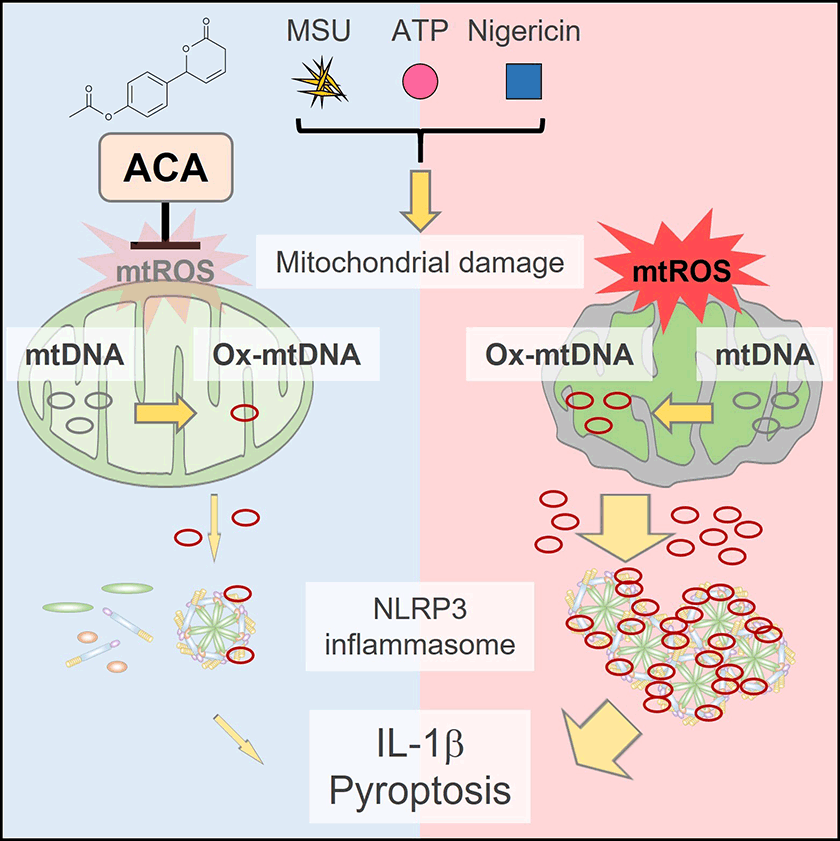
1'-Acetoxychavicol acetate inhibits NLRP3-dependent inflammasome activation by ameliorating mitochondrial damage
Molecular Immunobiology ・ Assistant Professor ・ Daisuke Ori
The formation (activation) of a cellular protein complex called the NLRP3 inflammasome plays a crucial role in the production of the inflammatory cytokine IL-1β. This process is closely associated with the pathogenesis of conditions such as atherosclerosis, gout, type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, and inflammatory bowel disease. Furthermore, it has been revealed in recent years that the NLRP3 inflammasome is activated in conjunction with mitochondrial impairment. We focused on 1'-Acetoxychavicol acetate (ACA), a component found in galangal used as a food ingredient and in pharmaceuticals. Our research discovered that ACA not only suppresses the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by inhibiting mitochondrial impairment but also mitigates pathological conditions such as gout and colitis.
Daisuke Ori NAIST Edge BIO, e0022. (2024).