2023.10.02
Novel functions of a unique protease working within cell membranes
Structural Life Science・ JSPS research fellow (PD) ・ Tatsuhiko Yokoyama
Intramembrane proteases are a group of unique proteases that hydrolyze membrane proteins within the hydrophobic phospholipid bilayer. We have recently shown that RseP, one of the intramembrane proteases of Escherichia coli, cleaves a single-pass transmembrane protein FecR to regulate cellular iron uptake(1) as well as several small membrane proteins (SMPs) to potentially modulate their functions(2).
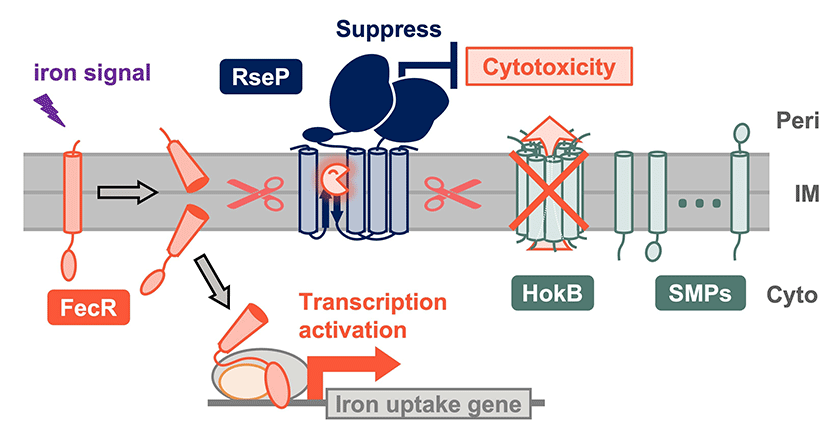
Figure. Novel substrates and functions of the E. coli intramembrane protease RseP
RseP cleaves FecR, a single-pass transmembrane protein, in response to an iron signal and the cleavage product functions to activate transcription of iron uptake genes. RseP also cleaves small membrane proteins (SMPs). RseP cleaves HokB, one of the SMPs, and suppresses its cytotoxicity. Peri, IM, and, Cyto indicate periplasm, inner membrane, and cytoplasm, respectively.
References
- Yokoyama, T., Niinae, T., Tsumagari, K., Imami, K., Ishihama, Y., Hizukuri, Y., and Akiyama, Y. (2021) The Escherichia coli S2P intramembrane protease RseP regulates ferric citrate uptake by cleaving the sigma factor regulator FecR. J Biol Chem. 296, 100673
- Yokoyama, T., Yamagata, Y., Honna, S., Mizuno, S., Katagiri, S., Oi, R., Nogi, T., Hizukuri, Y., and Akiyama, Y. (2023) S2P intramembrane protease RseP degrades small membrane proteins and suppresses the cytotoxicity of intrinsic toxin HokB. mBio. e0108623
Tatsuhiko Yokoyama NAIST Edge BIO, e0017. (2023).
